The urban heat island is a well-known phenomenon that affects all cities around the world. It is the difference in temperature between a city and the surrounding suburban area. In countries such as Greece, the peak summertime temperature difference between a city such as Athens and its periphery can be as much as 10 degrees Centigrade. The causes of this difference are multiple. In general, two of the main causes are the lack of natural green space in a city centre and the use of air conditioning for cooling.
Green roofs can cool a city such as Athens by a substantial amount—if we can install a sufficient number of them.
Natural green spaces that surround Greek cities lower the ambient temperature in those areas substantially. Over the last three decades, the use of air conditioning has grown and its implementation has accelerated. Air conditioning works by removing heat from inside a building and pumping it outside. This creates a vicious cycle. The air conditioning effectively heats the city while cooling the buildings internally. As the city gets hotter, more air conditioning is used to cool the buildings, making the city even hotter and increasing the requirement for cooling. Hotter cities mean more air conditioning, which means even hotter cities.
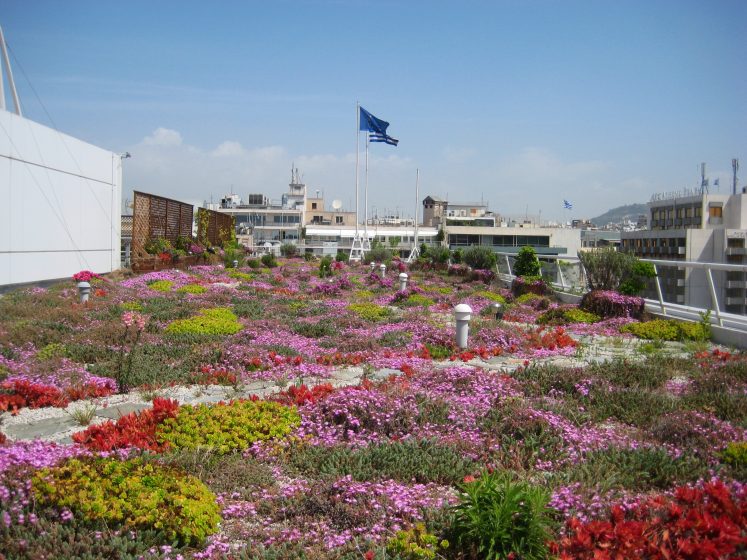

Studies conducted in Athens over the last thirty years have confirmed that the city is getting hotter over time and that air conditioning use is a major contributor to this heating. Other studies have shown that urban greening mitigates the urban heat island.
Cities in hot countries tend to have flat roofs and Athens is no exception. Currently, the rooftops typical of Athens, and of many other cities around the world, are a barren concrete wasteland of unused urban space. They represent a huge potential for greening.
A green roof is a perfect way to cool a building and also the surrounding space. A green roof cools a building in two ways. First of all, it shades the roof surface, protecting it from heat load and thereby reducing the temperature of the building. The second way a green roof cools a building is even more interesting in terms of city cooling. The plants on a green roof evapotranspire water through their leaves. This uses heat energy in the building. So the plants effectively remove heat from the building and, by extension, the city. Therefore, these two effects of green roofs lower both the temperature of the building and the temperature of the city. Consequently, less air conditioning is required and a “virtuous” cycle is established. Less air conditioning leads to less heat in the city, which, in turn, leads to a lowered requirement for air conditioning and on and on. How virtuous this cycle is depends on the amount of green roofs installed. The more green roofs the greater the cooling effect, the less air conditioning used and, consequently, the less heat produced and the more heat used.
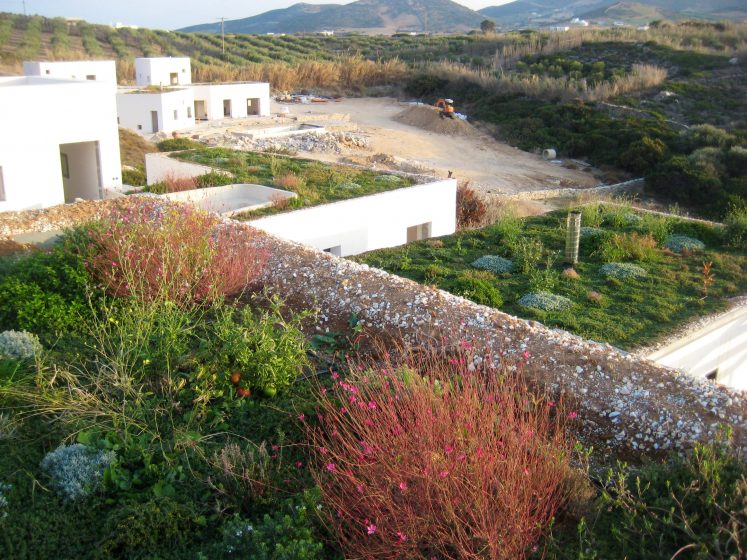

If this is all true, and research suggests it is, one must ask: when we will start to green the roofs of cities on a massive scale?

I am a believer in the power of the consumer. If we can get a critical mass of adopters, this could work. One idea would be for every resident of the city to fund and/or install one square metre of green roof on their building. Many of the apartment buildings in Athens have flat roofs of about 150 square metres and house 40 or more residents. So, under such a plan, each roof would have a total of 40 or more square metres of green roof. The total number of residents of Athens is five million. So that would be five million square metres of green space. This represents a green area bigger than the size of Central Park in New York (which is about 3.4 million square metres in area). This amount of cooling should lower the peak ambient temperature of the city to an extent that warrants much less use of air conditioning, yielding lower peak temperatures and less of a requirement for air conditioning; the aforementioned virtuous cycle kicks in. The point at which the virtuous cycle would start is not known empirically and is difficult to calculate because we are dealing with subjective human behaviour. A pilot study is required to prove the concept and, once proven, the concept would need effective communication to achieve a critical mass of adopters.
This is a simple way to cool a city appreciably. Once the model has been proven, it could be implemented worldwide. The one important consideration with this model is to not exchange the urban heat island problem for the bigger problem of water consumption. Appropriate green roofs should be installed and that means natural ecosystem green roofs which require much less irrigation, less other inputs, and less maintenance than inappropriate grass or sedum blanket roofs. Also, methods of winter rainwater harvesting for irrigation in the summer should be adopted.
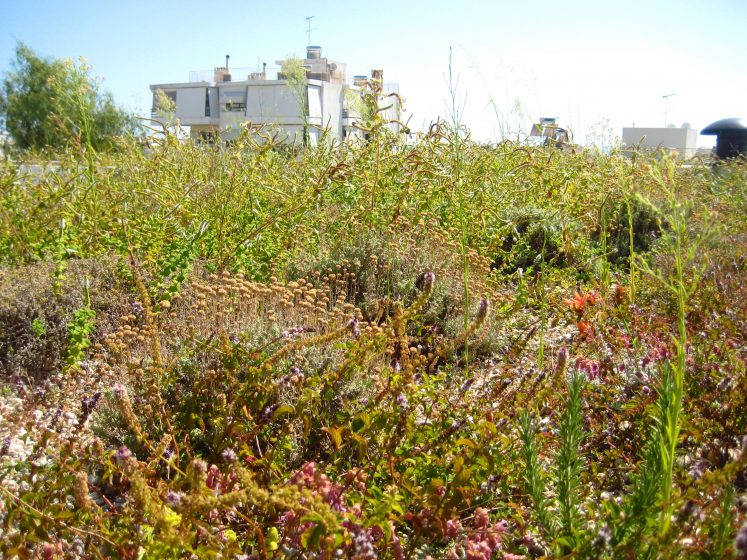
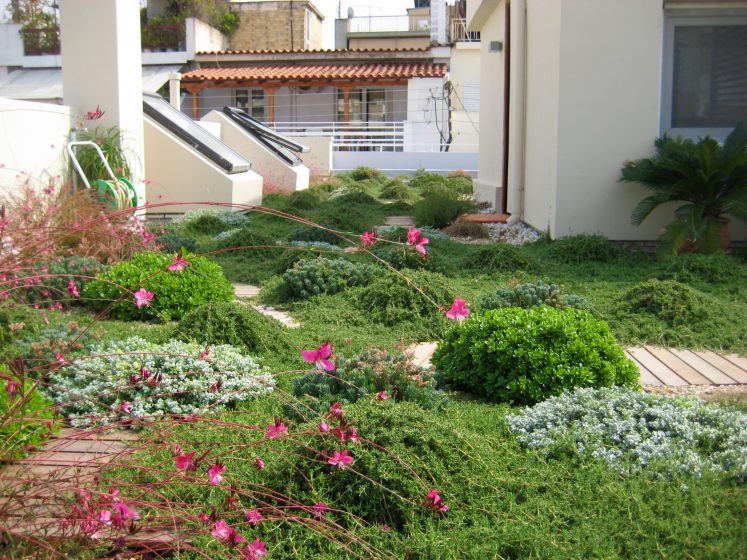


The opportunities that such a greening effort would provide are myriad, and include a wide range of business, employment, and recreational potentials not to mention the more important restoration of habitats for wildlife. In terms of business and employment opportunities, researchers of many varieties would be required to make the initiative a success, along with a list of green roof professionals, gardeners, installers, maintenance people, and so on. Communications and advertising professionals, as well as media people, would be required. Getting the public to support this idea is a matter of effective communication, in my opinion.
We could transform life in a city using this model with relatively little effort and with relatively little use of finite natural resources.
Andrew Clements
Corinth






Leave a Reply